openEuler FAQs
General
1. What is openEuler?
The OpenAtom openEuler project, short for openEuler, is an open-source OS project incubated and operated by the OpenAtom Foundation. It is a digital infrastructure OS that fits into any server, cloud computing, edge computing, and embedded deployment. This Linux distribution is compatible with multiple instruction set architectures and ideal for a wide range of operational technology applications, enabling OT-ICT convergence.
2. What is the openEuler community like?
Established officially on December 31, 2019, the openEuler community operates as a global hub for developers worldwide, aiming to foster an open, diverse, and architecture-inclusive software ecosystem tailored for wide-ranging digital infrastructure needs. openEuler collaborates closely with both upstream and downstream communities to ensure continuous tech improvement and timely release of new versions.
3. What instruction set architectures does openEuler support?
With active collaboration from leading chip vendors like Intel and AMD, openEuler supports multiple processor architectures, including x86, Arm, SW64, RISC-V, and LoongArch, with plans to expand to PowerPC.
openEuler is optimized for a wide range of CPU chips, such as Loongson 3 series, Zhaoxin KaiXian and KaiSheng, Intel Sierra Forest and Granite Rapids, and AMD EPYC Milan and Genoa. openEuler's compatibility extends beyond the CPU, encompassing NIC, RAID, Fibre Channel, GPU & AI, DPU, SSD, and security cards.
By offering a unified OS that can run on various devices, openEuler facilitates streamlined application development, allowing developers to target a wide range of hardware without significant code modification.
4. How often does openEuler release a new version?
openEuler releases two types of community versions: long-term support (LTS) and innovation versions.
LTS versions, like openEuler 20.03 LTS and openEuler 22.03 LTS, are released every two years and provide community support for four years. This includes two years of maintenance support and two years of extended support.
Innovation versions are released every six months, with each receiving community support for six months.
Prior to the end of any version's lifecycle, users will receive notifications from our mailing lists three months in advance.
5. What are openEuler's special interest groups all about? How can I join one?
The openEuler community is home to 100+ SIGs, each dedicated to a specific project or topic. These groups drive innovation in areas like toolchains, architectures, desktop environments, universal middleware, cloud-native infrastructure, and more! Our SIGs are hot on the heels of trends like AI, embedded systems, RISC-V, security, and compliance. They manage repositories, contribute to code, and even help shape community governance & operations.
You can find the full list of openEuler SIGs and their descriptions here.
Interested in joining an existing SIG? Send an email to the group's email address or contact the maintainers directly.
Can I start my own SIG? Absolutely! We have a simple and easy process for setting up a new SIG.
6. How can I contribute to openEuler?
Whether you're a coding whiz or an enthusiastic non-coder, there's a place for you in our community. Here's how to get started:
- Sign the CLA as an individual, employee or corporation.
- Head over to our SIG List to see ongoing projects and discussions. Join an existing SIG or start a new one.
- Submit/address issues, contribute code/packages/ projects, and participate in non-code contributions.
- Submit/Address issues on the QuickIssue page where you can sign in with your Gitee, GitHub, email, or other account.
- Contribute code to our source code repository on Gitee or our mirrored repository on GitHub. Rest assured, we review PRs regularly.
- Contribute packages/projects to our software package repository on Gitee or visit our website's Contribute Software Package page.
- Join in our community activities. We host a wide range of activities, including meetings, summits, live streams, and meetups.
Every contribution, big or small, is valued! Check out our contribution guide to learn more.
7. How can I stay informed about openEuler and chat with fellow users?
Here's how to stay informed about our developments and chat with fellow users:
- Visit our official website for usage guides and white papers.
- Explore our MOOCs for in-depth tutorials.
- Follow us on social media (LinkedIn, X, and YouTube) for the latest news on open source & OS industry events, partnerships, and technical solutions.
- Subscribe to our mailing lists to receive updates on SIG news.
- Engage in discussions and ask questions on the openEuler Forum or join the r/openEuler subreddit on Reddit for real-time communication. While the openEuler Forum's official English version is under construction, feel free to post in English on the existing forum and connect with other users!
8. Hmm, openEuler… Who's using it?
openEuler isn't just open-source — it's powering real innovation from semiconductors to a wide range of industries like operating systems, Internet, finance, carrier, electric power, manufacturing, energy, education, transportation, healthcare, and other fields. Companies tailor openEuler to their needs, creating commercial and enterprise distributions for both internal and external usage, and some of these companies have implemented large-scale deployments of these distributions.
We're all about making the future brighter and more open-source! Check out our success stories.
9. What can I implement using openEuler WSL?
You can implement the following using openEuler WSL:
- Deploy and use an openEuler LTS version on Windows.
- Create a smooth cross-platform development experience leveraging Visual Studio Code and openEuler WSL.
- Build a Kubernetes cluster in openEuler WSL.
- Use openEuler command-line programs or scripts to process files in Windows or WSL.
10. What does the hmdfs of openEuler do?
hmdfs stands for HarmonyOS Distributed File System. It is a soft bus-based distributed file system ported from the OpenHarmony community. hmdfs provides a globally consistent access view for each device dynamically connected to a network via the distributed soft bus (DSoftBus). It allows you to implement high-performance read and write operations on files using basic file system APIs, achieving low latency.
11. What is the SysCare of openEuler?
SysCare is a system-level hotfix software that provides security patches and hotfixes for OSs. It can fix system errors without requiring host restarts. SysCare combines kernel-mode and user-mode hot patching to manage system repairs, saving time for users to focus on other aspects of their business. In the future, live OS upgrades will be provided to enhance O&M efficiency.
12. What is A-Ops?
A-Ops is an OS-oriented O&M platform that provides intelligent O&M solutions covering data collection, health check, fault diagnosis, and fault rectification. The A-Ops project includes the following sub-projects: Gala (fault detection), X-diagnosis (fault locating), and Apollo (vulnerability rectification).
13. What capabilities does secGear provide?
secGear provides:
- Architecture compatibility: It masks differences between various SDK APIs by sharing the same set of source code across multiple architectures.
- Easy development: The development tools and general-purpose security components allow users to focus on services, significantly improving development efficiency.
- High performance: The switchless feature improves interaction performance between the rich execution environment (REE) and trusted execution environment (TEE) by more than 10-fold in typical scenarios, such as frequent REE-TEE interactions and big data interaction.
14. What security technologies are used in AI for OS?
Vulnerability discovery: Automatic vulnerability discovery is crucial to OS security. It identifies defects using code analysis, fuzz testing, or both. Traditional fuzz testing tools are often both random and blind when it comes to generating and selecting seeds, mutations, testing, and feedback. In addition, code analysis relies on defect pattern libraries, which need to manually be built by experts. AI improves this by detecting patterns in defect code datasets to enhance the precision and efficiency of vulnerability identification.
Intrusion detection: Modern security threats, such as Advanced Persistent Threats (APT), are sophisticated and persistent. Traditional security defenses often fail against unknown threats. AI enhances security by deeply analyzing data, extracting key features from high-dimensional datasets, and identifying system abnormalities effectively. This improves the accuracy and timeliness of attack blocking methods, such as in abnormal traffic and side-channel attack detection.。
15. What are the advantages of the multi-level scheduling framework provided by openEuler?
openEuler's multi-level scheduling framework allows you to choose the most suitable scheduling model for your needs and provides the following advantages:
- Higher flexibility and portability compared to traditional process/thread scheduling models.
- Faster model switching and scheduling thanks to the use of lightweight scheduling models.
16. How does openEuler ensure security?
openEuler ensures security by providing the following comprehensive security features:
- Authenticity protection
- Integrity protection
- Confidentiality protection
17. What security isolation technologies does openEuler provide for the industrial sector?
- Service isolation: Isolates potentially vulnerable services from known sources to minimize the impact of attacks on other system components.
- Code restriction: Limits code from untrusted sources to reduce potential harm to other system components.
18. What does "noise" in the openEuler operating system refer to?
Operating system noise includes non-application computing tasks executed during service running, such as:
- System/User-mode daemon processes
- Interrupt processing
- Processes in user mode or kernel
- Memory management and scheduling overhead
- Non-computing tasks in service applications (e.g., monitoring logs and thread communication)
- Resource competition (e.g., cache misses and page faults)
19. Where can I find common repo sources for openEuler?
You can find sorted and classified repo sources for various openEuler versions on the openEuler Forum.
20. When I install openEuler directly onto the second drive sdb, the system fails to start. How can I resolve this?
Installing openEuler on the second drive (sdb) results in both the MBR and GRUB defaulting to installation on sdb. The following two situations may occur:
- If the first drive sda contains a complete operating system, the system will boot from sda.
- If the first drive sda does not have a complete operating system, it may cause boot failure.
Both scenarios occur because the BIOS usually loads the bootloader from the first drive sda. If openEuler is not installed on sda, it will result in a boot failure.
This problem can be solved by either:
- During installation, when selecting the drive (whether the first or both drives), specify to install the bootloader on the first drive sda.
- After the system is installed, if your BIOS allows selecting the boot drive, you can modify the BIOS boot order and then reboot the system.
21. If openEuler enters emergency mode upon boot, what steps should I take next?
If the openEuler enters emergency mode upon boot.
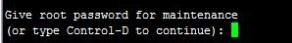
It indicates issues such as file system corruption causing drive mounting failures, overpressured I/O leading to drive mounting timeout (threshold: 90s), or anomalies like unexpected power-off or low I/O performance of drives. To solve this issue:
Log in to openEuler as the root user.
Check and restore files by using the file system check (fsck) tool, and reboot openEuler.
 NOTE
NOTEThe fsck tool checks and maintains inconsistent file systems. In case of power-off or drive issues, fsck commands can be used to check file systems. Run the
fsck.ext3 -handfsck.ext4 -hcommands to view the usage instructions for fsck.
To cancel drive mounting timeouts, add x-systemd.device-timeout=0 to the etc/fstab file. For example:
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Mon Sep 14 17:25:48 2015
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/drive'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/openEuler-root / ext4 defaults,x-systemd.device-timeout=0 0 0
UUID=afcc811f-4b20-42fc-9d31-7307a8cfe0df /boot ext4 defaults,x-systemd.device-timeout=0 0 0
/dev/mapper/openEuler-home /home ext4 defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/openEuler-swap swap swap defaults 0 022. What should I do when openEuler fails to reinstall due to drive failure caused by inactivated logical volume groups?
Before reinstalling openEuler, any inactivated logical volume groups must be restored to a normal state or clear them to avoid exceptions during the reinstallation process. For example:
Restore the logical volume group.
Run the following command to clear the activation status of the volume group to ensure that the error message "Can't open /dev/sdc exclusively mounted filesystem" is not displayed:
shvgchange -a n testvg32947Run the following command to recreate a physical volume based on the backup file:
shpvcreate --uuid JT7zlL-K5G4-izjB-3i5L-e94f-7yuX-rhkLjL --restorefile /etc/lvm/backup/testvg32947 /dev/sdcRun the following command to restore the volume group information:
shvgcfgrestore testvg32947Run the following command to reactivate the logical volume group:
shvgchange -ay testvg32947
Clear the logical volume group. Run the following commands:
shvgchange -a n testvg32947 vgremove -y testvg32947
23. What should I do if an error occurs when selecting the installation source?
If you encounter the message "Error checking software selection," it may indicate that certain software package dependencies are not met. Please ensure the installation source is valid. If not, consider switching to an alternative source.
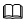
24. How do I enable the kdump service?
Reserved memory is necessary for running the kdump kernel. If the output of systemctl status kdump is "No memory reserved for crash kernel", follow the steps below to reserve it.
- Add crashkernel=1024M, high to /boot/efi/EFI/openEuler/grub.cfg (see the table below for details).
- Restart the system to apply the modification.
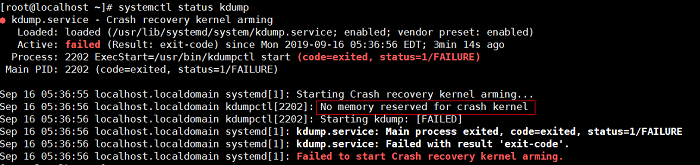
- Run
systemctl status kdumpto check the kdump status. If "active" is displayed in the output, as shown in the following figure, the kdump service is enabled.
crashkernel values
| Parameter | Description | Default Value | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| crashkernel=X | Reserves X physical memory for kdump if total memory is less than 4 GB. | None | Use this configuration only when the total memory is less than 4 GB and ensure sufficient continuous memory. |
| crashkernel=X@Y | Reserves X memory starting from address Y for kdump. | None | Ensure the X memory starting from address Y is not reserved for other modules. |
| crashkernel=X,high | Reserves 256 MB physical memory for kdump if the physical memory is less than 4 GB, and X physical memory if 4 GB or more. | None; recommended value: 1024M,high | Ensure continuous 256 MB memory for physical memory under 4 GB, and X continuous memory for 4 GB or more. Actual reserved memory: 256 MB + X. |
| crashkernel=X,low crashkernel=Y,high | Reserve X physical memory for kdump if the physical memory is less than 4 GB, and Y physical memory if 4 GB or more. | None | Ensure continuous X physical memory for physical memory under 4 GB, and continuous Y memory for 4 GB or more. Actual reserved memory: X + Y. |
25. Why can't I select a single drive for openEuler installation when multiple drives form a logical volume?
It is likely you have encountered the following error.
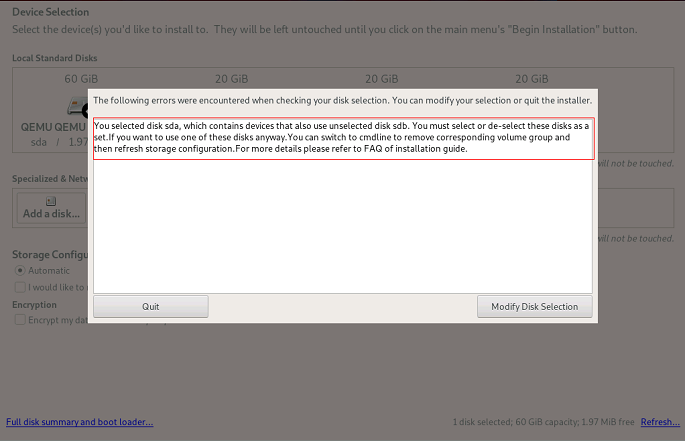
This occurs because the drive is part of a logical volume. Modifying one drive can corrupt the entire volume. openEuler prevents OS installation on such drives and shows an error message.
To use the drive, delete the volume group corresponding to the logical volume first:
Press Ctrl+Alt+F2 to switch to the CLI and run
vgsto find the volume group, for example, euleros.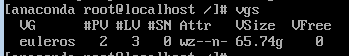
Run
vgremove eulerosto delete the volume group.Run
systemctl restart anacondato restart the system for the modification to take effect. NOTE
NOTEYou can also press Ctrl+Alt+F6 to return to the GUI and click Refresh in the lower right corner to update the storage configuration.
26. What should I do if I cannot install openEuler on an x86 physical machine due to the BIOS security boot option?
When you install openEuler on an x86 machine and the BIOS setting for secure boot is enabled (which is usually disabled by default), the system might get stuck on the "no bootable device" screen, as shown below, halting installation.
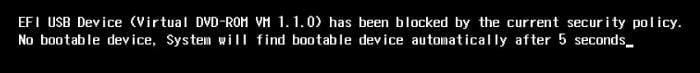
This occurs because, with secure boot activated, the mainboard checks the digital signatures of the bootloader and OS. If they are not signed with the right private key, the built-in public key of the mainboard will prevent them from running.
To proceed with the installation, disable secure boot:
Press F11 as the system starts up and input the password Admin@9000 to enter the BIOS.

Select Administer Secure Boot.

Set Enforce Secure Boot to Disabled.
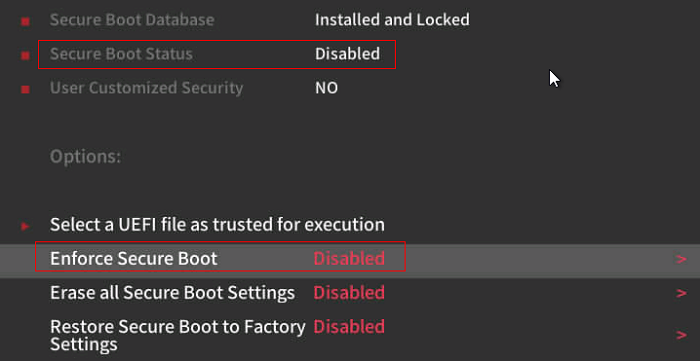
Save the changes and exit. You should now be able to install openEuler successfully.
27. How should I address the appearance of "pmie_check failed in /usr/share/pcp/lib/pmie" in the "messages" logs following the openEuler installation with the "Server - Performance tools" software option?
The Anaconda installer, used during openEuler installation, cannot install SELinux policy modules within its chroot environment. Consequently, when the "Server - Performance tools" option installs PCP-related software packages, including pcp-selinux, the necessary SELinux policy module is not applied, resulting in an error. To resolve this issue, execute one of the following commands after installing and restarting openEuler:
- Install the pcpupstream SELinux policy module directly:
# /usr/libexec/pcp/bin/selinux-setup /var/lib/pcp/selinux install "pcpupstream"- Reinstall the pcp-selinux package:
# sudo dnf reinstall pcp-selinux28. What should I do if the openEuler installation fails after I select two drives that already have an OS installed, and then customize the partitions?
If there are two drives with an OS already installed, selecting the first drive for partitioning and then canceling, followed by selecting the second drive and partitioning, will lead to installation failure.
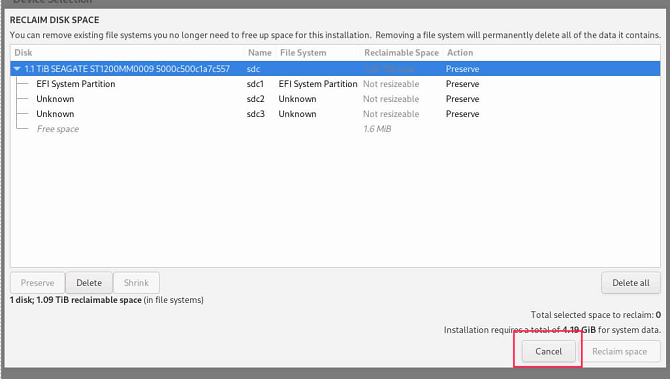
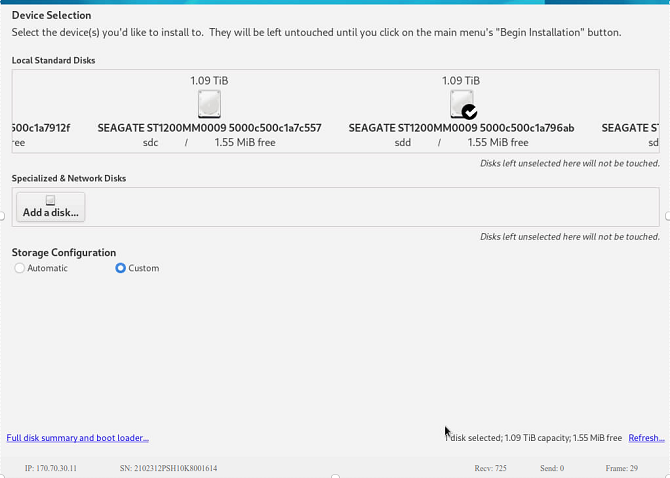
This is because frequent operations can corrupt drive information. You are advised to directly select the target drive for partitioning. If you must cancel and reselect, it is recommended that the installation process be started from the beginning.
29. What should I do if kdump cannot generate vmcore on a physical machine with an LSI MegaRAID card?
After kdump is deployed, the system fails to generate a vmcore file following a kernel crash, either triggered manually (using echo c > /proc/sysrq-trigger) or due to a system fault. While kdump attempts to boot the second kernel, the MegaRAID driver throws error "BRCM Debug mfi stat 0x2d, data len requested/completed 0x200/0x0", as shown in the image below.
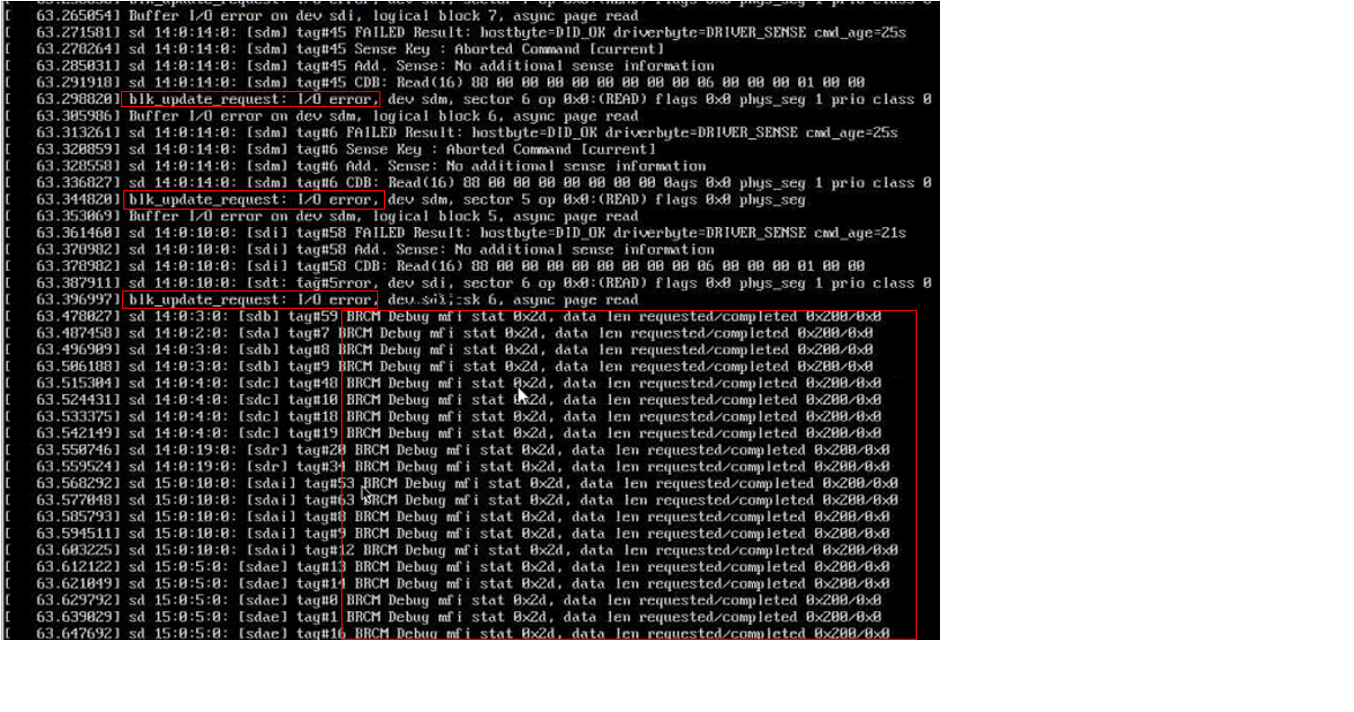
The issue stems from the default reset_devices boot parameter. When the second kernel boots, it triggers a device reset as part of its initialization. This reset operation can cause the MegaRAID card or the connected drives to enter an error state. Consequently, when kdump tries to write the vmcore file to the drives managed by the MegaRAID card, it encounters errors, preventing the vmcore generation.
To resolve this issue, you need to remove the reset_devices parameter from the boot configuration of the second kernel:
- Open the kdump configuration file /etc/sysconfig/kdump.
- Locate the line where the kernel boot parameters are defined.
- Remove the reset_devices parameter.
- Save the changes.
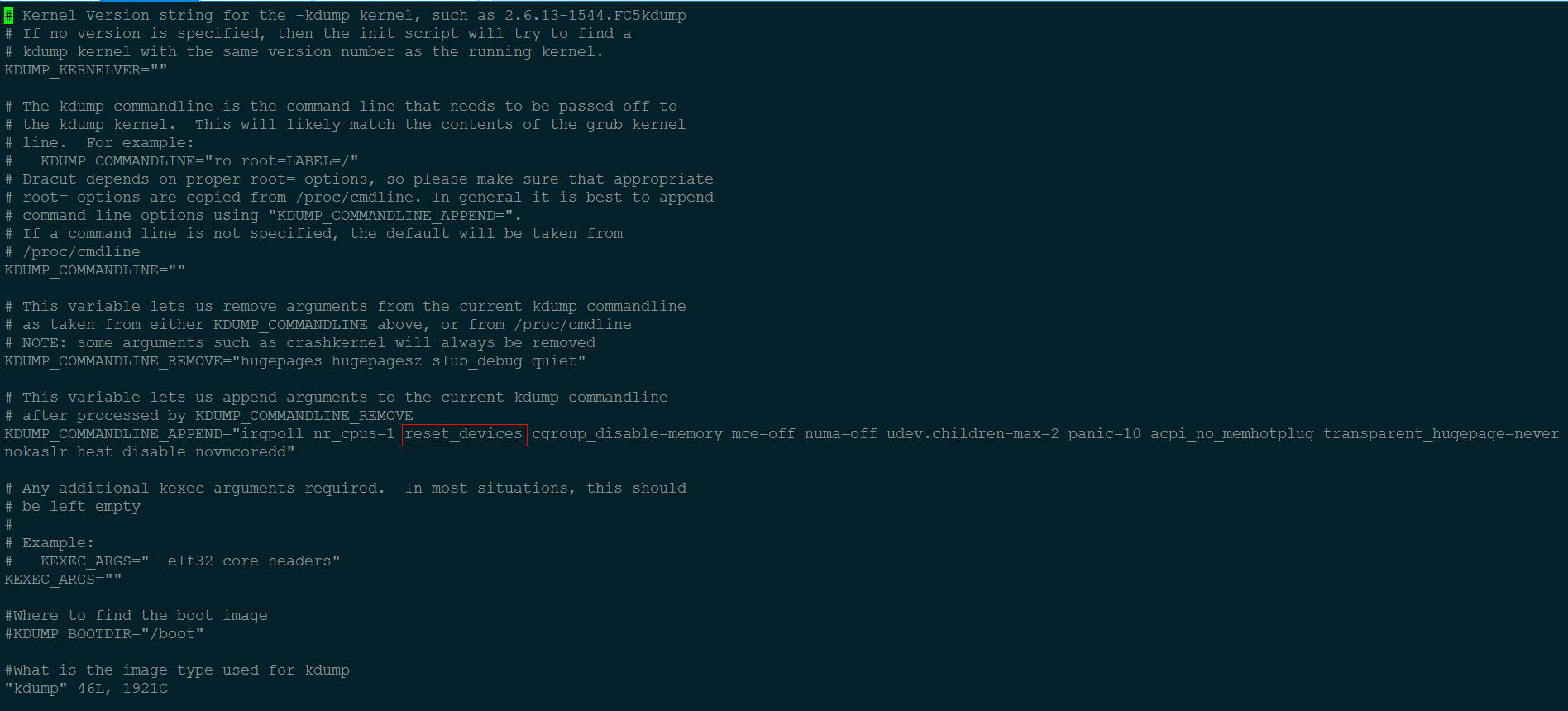
By removing the reset_devices parameter, you prevent the device reset operation during the second kernel boot process. This, in turn, avoids the MegaRAID driver error related to incomplete I/O requests, allowing kdump to successfully generate the vmcore file.
30. Why does the Raspberry Pi fail to start after I write the openEuler image to the SD card?
This could be due to:
Incomplete image. Verify the integrity of the downloaded image.
Corruption during image writing, especially on Windows. Try writing it on another OS.
31. Why can't I connect to Wi-Fi using the nmcli command?
If you encounter the error message "Error: Connection activation failed: (7) Secrets were required, but not provided," it indicates that the password is missing in the nmcli dev wifi connect SSID password PWD command. To resolve this issue, ensure that the password is included in the command. If the password contains special characters, remember to enclose it in single quotation marks. If this solution does not work, you can also try using the nmtui utility.
- Run
nmtuito enter the text-based user interface (TUI) of nmtui. - Select Edit a connection and press Enter to open the network connection editing window.
- Select Add and press Enter to add a connection.
- Select Wi-Fi then Create to configure Wi-Fi information.
- Configure the following fields. Other fields are optional.
- Profile name: name of the Wi-Fi connection
- Device: NIC to use for the connection (enter wlan0)
- SSID: SSID of the Wi-Fi network to connect
- Security: Wi-Fi encryption mode (select one as required, for example, WPA & WPA2 Personal)
- Password: password of the Wi-Fi network
- After creating the connection, select Back to go back to the TUI home page.
- Select Activate a connection and press Enter.
- The Wi-Fi connection will be marked with * if activated. If not, move the cursor to the connection, then select Activate. Once the connection is activated, select Back to go back to the nmtui TUI home page.
- Select Quit then OK to exit nmtui.
32. How do I correctly install TensorFlow and related packages?
TensorFlow 2.12.1 installation may fail if dependencies are not updated to support it. Manually install the dependencies as follows:
- Run
yumdownloader python3-tensorflowto download the TensorFlow RPM package. - Run
rpm -ivh --nodeps python3-tensorflowto install the package. - Install dependencies of TensorFlow:
- Use
pip3for some dependencies:pip3 install tensorflow-estimator==2.12.0 keras==2.12.0 protobuf==3.20.3 - Use
yumfor other dependencies:yum install python3-termcolor python3-future python3-numpy python3-six python3-astunparse python3-google-pasta python3-opt-einsum python3-typing-extensions python3-wrapt python3-h5py python3-grpcio python3-absl-py python3-flatbuffers python3-gast
- Use
- Use
yumto install related packages, for example,yum install python-keras-rl2.
33. Does openEuler support Btrfs, bcachefs, and ZFS?
openEuler currently supports Btrfs but it's worth noting that Btrfs support may change in the future due to relatively low user engagement. If you have feedback or suggestions, consider subscribing to our kernel SIG mailing list at kernel@openeuler.org here to share your thoughts.
If the above FAQs cannot resolve your issue, please send an email to our mailing lists describing your issue or discuss it on the openEuler Forum also you can submit your issue on the QuickIssue.
